A Labor Compliance Roundup
Here is brief look at updated Labor Compliance laws as of January 2022. We cover everything from COVID-19 compliance to state and local initiatives. While our “Roundup” does not provide legal advice, it does seek to alert our customers to the myriad of issues and challenges that arise in our industry.
COVID-19 Updates
Nevada Paid COVID-19 Vaccination Leave, Effective June 2021
Effective June 9, 2021, through December 31, 2023, private employers in Nevada with 50 or more employees must provide all employees with up to four total hours of paid leave for the purpose of receiving a COVID-19 vaccine. Employees receiving a single-dose vaccine are entitled to use only two consecutive hours of vaccination leave, while employees receiving two doses are entitled to use two consecutive hours of vaccination leave per injection. Employers that provide a clinic on their premises where the employee can be vaccinated for COVID-19 during regular work hours, as well as employers in their first two years of operation, are exempt from these requirements.
Additional information is available here.
Cook County, Illinois Passes Ordinance Requiring Paid Leave for COVID-19 Vaccination, Effective July 2021
Employers with Illinois-based employees should be aware of the new Cook County ordinance that requires they provide paid time off for workers getting vaccinated. The ordinance covers all of Cook County, including the city of Chicago. The ordinance covers all private entities that employ at least one person and have a principal place of business within Cook County or do business within the county.
There are two important things to note about the new ordinance:
- If the employer implements a vaccination mandate, the employee must receive compensation for up to four hours.
- If the employer does not mandate a vaccination, the employee would only be allowed to use any accrued, unused, and available sick time or paid time off for the purpose of receiving a vaccine.
The ordinance went into effect on July 1, 2021 and remains in effect until the Director of the Cook County Public Health Department determines in writing that the public health threat from COVID-19 has reduced to the level that the ordinance can be repealed.
Additional information is available here.
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Enacts Another Emergency Paid Sick Leave Ordinance, Effective July 2021
Employers with 50 or more employees are required to provide up to 80 hours of emergency paid sick leave to full-time employees for certain COVID-19-related reasons. 626B was passed as a new law, but it is nearly identical to Pittsburgh’s original Temporary COVID-19 Emergency Paid Sick Leave Ordinance (626A), which was in effect from December 8, 2020, to June 17, 2021.
Additional information is available here.
COVID-19 Designated as an Airborne Infectious Disease Under New York State's HERO Act, Effective September 2021
On September 6, 2021, Governor Kathy Hochul announced the designation of COVID-19 as an airborne infectious disease under the HERO Act. This designation sets in motion the requirement for all employers to implement workplace safety plans previously put in place.
Additional information is available here.
Massachusetts Extends and Expands COVID-19 Emergency Paid Sick Leave, Effective October 2021
On May 28, 2021, Massachusetts enacted an emergency paid sick leave law, providing every full-time employee up to 40 hours of job-protected emergency paid sick leave for specified COVID-19-related reasons. The law also created a $75 million COVID-19 Emergency Paid Sick Leave Fund to reimburse eligible employers for providing their employees with this additional emergency paid sick leave. The paid leave entitlement was set to expire on September 30, 2021, or when the fund was exhausted. This amendment extends the effective period of the leave entitlement to April 1, 2022, or whenever the fund is exhausted.
The law originally permitted employees to use the leave to obtain a diagnosis, care, or treatment for COVID-19 symptoms. The amendment expands the permissible reasons for using leave to include obtaining the COVID-19 vaccination and any recovery related to the immunization.
Additional information is available here.
Federal Laws
Federal Tax Credits
The federal Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has announced that certain employers can claim federal tax credits when employees use emergency paid leave to accompany an individual to obtain a COVID-19 vaccination and/or to care for an individual recovering from an injury, disability, illness, or condition related to the vaccine. This credit is available for certain private employers with 499 or fewer U.S. employees and certain public employers that are voluntarily providing employees emergency paid leave for various COVID-19-related reasons. Eligible employers may claim tax credits for sick and family leave paid to employees for leave taken from April 1, 2021, through September 30, 2021.
Additional information is available here.
COVID-19 Vaccination and Testing; Emergency Temporary Standard, Effective January 2022
Employers of 100 or more employees are required to implement a mandatory COVID-19 vaccination policy, with an exception for employers that instead adopt a policy requiring employees to either get vaccinated or elect to undergo regular COVID-19 testing and wear a face covering at work in lieu of vaccination. Medical and religious exemptions remain available to those who qualify. All covered employees must be fully vaccinated or commence weekly COVID-19 testing by January 4, 2022. A U.S. circuit court stay has been lifted as of December 17, 2021, and the Supreme Court is set to hear legal challenges on January 7, 2022. Please continue to consult with your legal counsel concerning updates.
Additional information is available here.
State and Local Laws
Illinois SB 1480 Pay Data Reporting Law Gets Amended, Effective June 2021
On June 25, 2021, Illinois SB 1480 was amended by SB 1487 to provide clarification on how Illinois employers must comply with the new equal pay requirements. There are three critical parts to SB 1480: (1) the “Equal Pay Registration Certificate,” (2) public-facing employee demographic data reports, and (3) a prohibition on the use of conviction records as the basis of employment decisions.
Additional information is available here.
Louisiana To Require Reasonable Accommodations for Pregnancy, Effective August 2021
Act No. 393 amends the Louisiana Employment Discrimination law, modifying its prohibition on pregnancy discrimination to include a responsibility to provide reasonable accommodations for physical limitations related to pregnancy. These new rules will apply to all employers with 25 or more employees.
Additional information is available here.
Louisiana Passes Law on Criminal Background Checks, Effective August 2021
The state of Louisiana has passed a law—Act No. 406 (HB 707)—that affects businesses conducting background checks on applicants before offering them a job by prohibiting employers from requesting or considering an arrest record or charge that did not result in a conviction when a background check reveals that information. Employers are required to individually assess the criminal histories of applicants and determine if there is a direct and adverse relationship with the specific duties of the job to deny them the position. During the “individualized assessment,” employers must apply three factors: (1) the nature and gravity of the offense or conduct, (2) the time that has elapsed since the offense, conduct, or conviction, and (3) the nature of the job sought.
Additional information is available here.
The District of Columbia Expands Paid Family Leave Program, Effective October 1, 2021
Eligible individuals may now also take up to two workweeks of prenatal leave for newly added qualifying reasons, separate from and in addition to parental leave that had already been available under the program. The new qualifying reasons for prenatal care include:
- Routine and specialty appointments, exams, and treatments associated with a pregnancy provided by a health care provider, including prenatal check-ups and ultrasounds.
- Treatment for pregnancy complications.
- Bedrest that is required or prescribed by a health care provider.
- Prenatal physical therapy.
In addition, employees are now eligible for six weeks of medical leave, rather than the previous two weeks.
Additional information is available here.
Washington Creates Long-Term-Care Program
Washington requires employers to withhold employee premiums via payroll deductions and remit them to the state Employment Security Department for the state's long-term-care program. The plan, signed into law in 2019 with the Long-Term Care Trust Act, will use a 0.58% payroll tax to provide up to a $36,500 benefit for individuals to pay for home health care and an array of services related to long-term health care, including equipment, transportation, and meal assistance. The Washington Cares Fund was originally set to begin collecting taxes in January 2022. However, on Friday December 17, Governor Jay Inslee announced a decision to delay the start of the mandatory payroll tax.
Additional information is available here.
Additional Updates for 2022
IRS Issues Standard Milage Rates for 2022
Notice 2022-03, December 17, 2021
Today, the Internal Revenue Service issued the 2022 optional standard mileage rates used to calculate the deductible costs of operating an automobile for business, charitable, medical or moving purposes.
Beginning on January 1, 2022, the standard mileage rates for the use of a car (also vans, pickups, or panel trucks) will be:
- 58.5 cents per mile for business purposes.
- 18 cents per mile for medical or moving purposes.
- 14 cents per mile for charitable purposes.
The new mileage rates are up from 56 cents per mile for business purposes and 16 cents per mile for medical or moving purposes in 2021.
The standard mileage rate for business use is based on an annual study of the fixed and variable costs of operating an automobile. The rate for medical and moving purposes is based on the variable costs.
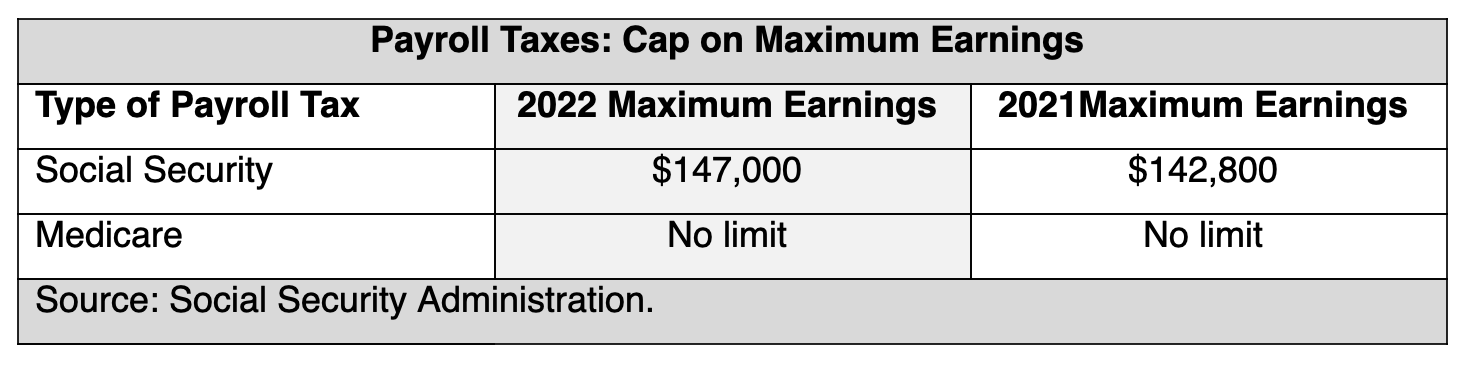
Social Security Tax Limits for 2022
Starting January 1, 2022, the maximum earnings subject to the Social Security payroll tax will increase by $4,200 to $147,000—up from the $142,800 maximum in 2021. Check out the Social Security Administration (SSA)’s October 13 announcement here. The SSA also posted a fact sheet summarizing the 2022 changes, which you can view here.
The taxable wage cap is subject to an automatic cost-of-living adjustment (COLA) each year based on increases in the national average wage index, calculated annually by the SSA.
401K Limits for 2022
The IRS recently announced that the 2022 contribution limit for 401k plans will increase by $1,000 to $20,500, up $19,500 from 2021.
- The 401 (k)-contribution limit is $20,500.
- The 401 (k) catch-up contribution limit remains unchanged at $6,500 for those aged 50 and older.
- The limit for employer and employee contributions will increase to $61,000.
Georgia Loan-Out Backup Withholding Rate for 2022
Georgia loan-out rate remains at 5.75% for 2022.
New Mexico Loan-Out Withholding Rate for 2022
The new loan-out state backup withholding will remain at 5.9% in 2022.
PHBP – Producer’s Health Benefit Plan for Commercial Production Employees
Minimum contribution amount remains at $45.00 per day.
Download These Helpful Guide


-2.png)
